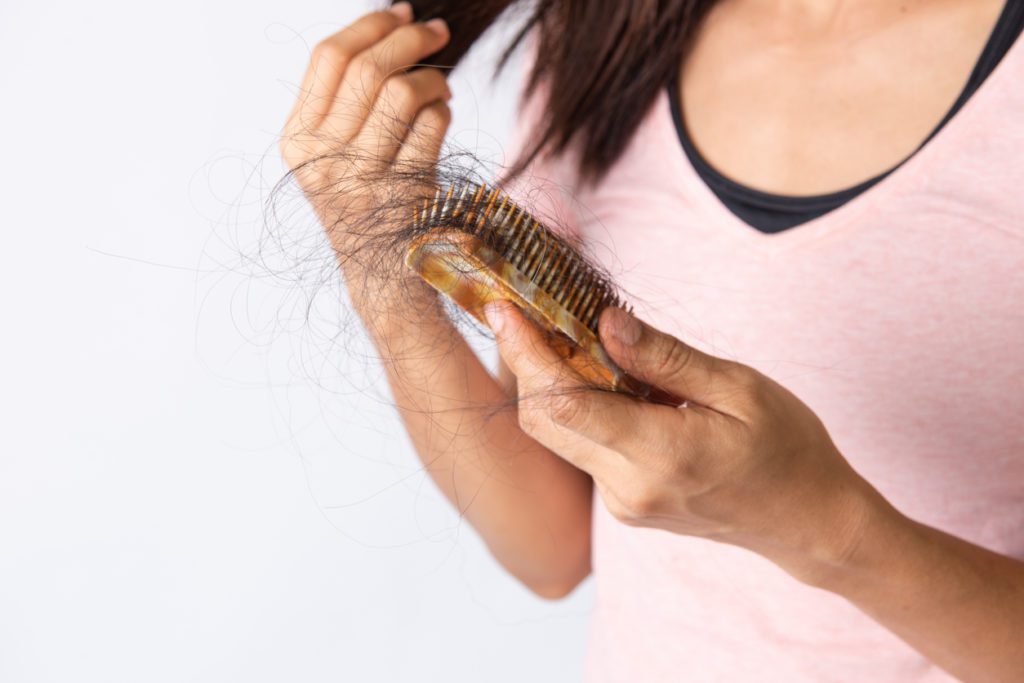
A long list of factors, such as anxiety, ageing, and some illnesses, can cause hair loss. We understand that it can be an embarrassing and life-changing thing to go through, especially for women, which is why we do our best to assist those who need our help.
However, we also understand that each patient and their circumstances are different, and some causes for hair loss require additional input from other medical professionals outside the cosmetics industry.
So, today we’re exploring hair loss after illness and what we suggest you do to tackle the problems that come with this.
Which Illnesses Cause Hair Loss and Why Is This?
Many different illnesses can cause hair loss, including, but not limited to the following:
- Autoimmune diseases, such as alopecia areata and lupus. Hair loss occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells and tissues, including the hair follicles. This attack then causes the hair to fall out in small, round patches on the scalp, face, and other areas of the body.
- Hormonal imbalances, such as thyroid disorders or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). In PCOS, there is an excess production of androgens, which are male hormones also present in women in small amounts. The high levels of androgens can cause hair follicles to shrink and produce shorter, thinner hair, leading to hair loss.
- Fungal infections of the scalp can cause inflammation of the hair follicles, weakening them and causing hair to fall out.

- Skin conditions like psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis can cause hair loss when they occur on the scalp because they can interrupt the hair growth cycle. In addition, seborrheic dermatitis can cause excessive oil production and clog hair follicles, which prevents hair from growing.
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as iron or vitamin D deficiency. These vitamins and nutrients play a vital role in your hair growth cycle, so without them, the hair struggles to grow.
- Cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. They cause hair loss by damaging rapidly dividing cells in the body, including hair follicle cells. Although the treatments target cancer cells, they can also damage healthy cells, including those in hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
- Certain medications, such as blood thinners, antidepressants, or beta-blockers, cause hair loss by altering the normal hair growth cycle, usually by changing hormone levels in the body.
Overall, hair loss can result from damage to hair follicles, an imbalance of hormones or scalp inflammation, and the treatment for hair loss will depend on the underlying cause.
COVID-19 and Hair Loss
There have been links between COVID-19 and hair loss since early 2020 when the pandemic hit, but it’s unclear what this link means. Research has suggested that hair loss may be due to a number of reasons, such as physical or emotional stress caused by the illness, as well as potential nutritional deficiencies or medication use.
Again, it’s not clear exactly what this link means, but we suggest consulting with your GP if you are experiencing hair loss that you believe is related to COVID-19 before seeking treatment externally.

Does Hair Loss Caused by Illness Look Different to Other Causes of Hair Loss?
In general, hair loss caused by illness may not look different from other causes. However, the specific pattern and appearance of hair loss can depend on the underlying condition causing it. For example, certain autoimmune disorders may cause hair loss in a patchy or uneven pattern, while other conditions may result in more diffuse hair loss. Therefore, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of hair loss before visiting a cosmetic clinic such as ourselves for treatment.
How Can You Treat Hair Loss?
There are various ways you can treat hair loss after illness, but once you have recovered from the cause of your hair loss, you are able to seek our help. Here at Aesthetic Skin Clinic, we offer Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) treatment at our clinics in Jersey and Guernsey.
PRP is a concentrated solution of platelets extracted from an individual’s blood. Platelets are a natural component of blood and contain growth factors and cytokines that promote healing and regeneration. The PRP procedure involves drawing a person’s blood, which is then separated using a centrifuge to isolate the different components. The resulting PRP is then injected into the area experiencing hair loss. Over a period of several months, new hair growth should occur if the hair follicles are still viable, and improvements will continue for 3-6 months.

Dealing With Hair Loss Mentally
Although we can do our best to treat the physical effects of hair loss, we can’t help with any adverse mental side effects, and it’s important that you’re aware of this before seeking our treatments.
When it comes to dealing with hair loss mentally, we understand it can be a struggle, which is why confiding in someone and sharing your worries and concerns is crucial. Talk to a trusted friend or family member about your feelings surrounding your hair loss, or discuss your worries with a professional, such as a counsellor or support group, if you feel you need additional help.
Of course, our fully trained medical professional team are here to support you if you choose to go through with our PRP treatment, and we will ensure you’re happy at every stage of your treatment to guarantee the best results.
If this sounds like something that would help you deal with hair loss after illness, please feel free to get in touch, and a member of our team will be more than happy to help.